There are many different methods of contraception available to prevent pregnancy, both hormonal and non-hormonal, but the ONLY method of contraception that prevents STIs is condoms. In order to prevent unwanted pregnancies and STIs it is advisable to use two forms of contraception, for example, the oral contraceptive pill and a condom, or the contraceptive injection and a condom, in order to protect you and your partner.
Below is a breakdown of the different methods of contraception that are available along with their advantages and disadvantages. Unfortunately, no contraceptive method, except abstinence, is considered to be 100% effective.
Hormonal Contraceptives
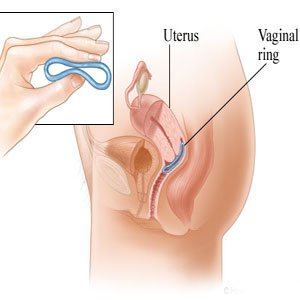
Vaginal Ring
A small, plastic ring is placed in the vagina, releasing oestrogen and progestogen. A new ring is inserted each month for three out of four weeks. It is 91% effective in preventing pregnancy with typical use.
Advantages:
Periods can become regular, lighter, and less painful
Can improve skin
Disadvantages:
You need to insert and remove it yourself
Is not safe for use with certain medical conditions
Contraceptive Patch
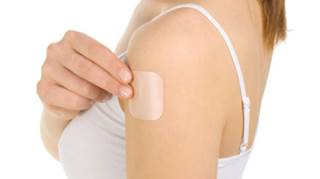 A patch is stuck on the skin and releases oestrogen and progestogen. It is replaced once a week for three weeks, followed by a patch free week. It is 91% effective in preventing pregnancy with typical use.
A patch is stuck on the skin and releases oestrogen and progestogen. It is replaced once a week for three weeks, followed by a patch free week. It is 91% effective in preventing pregnancy with typical use.
Advantages:
Periods can become regular, lighter, and less painful
Can improve skin
Can be worn discreetly
Disadvantages:
Can cause skin irritation
Is not safe for use with certain medical conditions
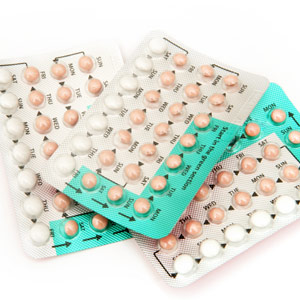 Combined Oral Contraceptive Pill
Combined Oral Contraceptive Pill
The pill contains oestrogen and progestogen. You must take a pill at roughly the same time everyday. It is 91% effective in preventing pregnancy with typical use.
Advantages:
Can make periods regular, lighter, and less painful
Allows you to predict your next period
Can allow you to skip periods
Can improve skin
Disadvantages:
Have to take a pill everyday
Might not be effective if you vomit, have severe diarrhoea, or take certain medications
Not effective if two or more pills have been missed
Is not safe for use with certain medical conditions
Progestogen-Only Pill
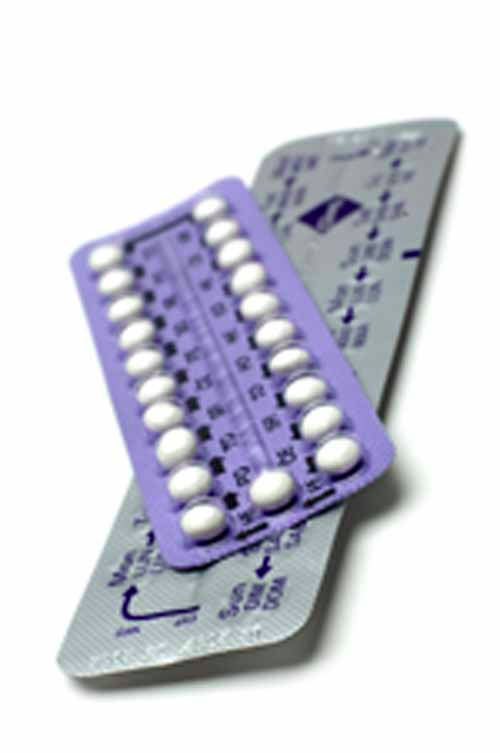 This pill contains progestogen and is generally for women who cannot use the combined pill for medical reasons. A pill must be taken at roughly the same time everyday. It is 91% effective in preventing pregnancy with typical use.
This pill contains progestogen and is generally for women who cannot use the combined pill for medical reasons. A pill must be taken at roughly the same time everyday. It is 91% effective in preventing pregnancy with typical use.
Advantages:
Periods may be lighter or stop
Disadvantages:
Have to take a pill everyday
Periods may be irregular or more frequent
Might not be effective if you vomit, have severe diarrhoea, or take certain medications
Generally not effective if taken over three hours late
 Contraceptive Injection (Depo-Provera, Sayana Press or Noristerat)
Contraceptive Injection (Depo-Provera, Sayana Press or Noristerat)
The injection contains progestogen. You will need to attend your local clinic to receive the injection every eight, twelve, or thirteen weeks, depending on the type of injection. It is 94% effective in preventing pregnancy with typical use.
Advantages:
Periods may stop
Disadvantages:
In some, periods become irregular or last longer
Need to attend regular appointments to receive injections
 Contraceptive Implant (Implanon or Nexplanon)
Contraceptive Implant (Implanon or Nexplanon)
After administration of local anaesthetic, a small rod is inserted under the skin of the upper arm by a doctor. The implant releases progestogen. It is 99.95% effective in preventing pregnancy.
Advantages:
Don’t have to remember to take a pill everyday
Periods can stop
Disadvantages:
Can cause acne
In some, periods become irregular or last longer
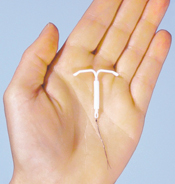 Intrauterine System (Mirena or Jaydess)
Intrauterine System (Mirena or Jaydess)
A small plastic device that releases progestogen. It can be inserted as a day procedure at your local clinic. A speculum will be inserted into your vagina (just like a Pap Smear) so that the doctor can insert the device into your uterus. You can take some over-the-counter pain relief prior so that the procedure is not too painful. Before you can have it inserted, your doctor will do a pregnancy and STI test. It is 99.8% effective in preventing pregnancy.
Advantages:
Don’t have to remember to take a pill everyday
Lasts for five years
Periods can become lighter and less painful
Disadvantages:
Can experience irregular bleeding in the fist six months
Non-hormonal Contraceptives
Intrauterine Device (the coil) A small copper device is inserted into the uterus by a doctor. There are no hormones involved. The procedure for insertion is the same as for the Intrauterine System. It is 99.2% effective in preventing pregnancy.
A small copper device is inserted into the uterus by a doctor. There are no hormones involved. The procedure for insertion is the same as for the Intrauterine System. It is 99.2% effective in preventing pregnancy.
Advantages:
Don’t have to remember to take a pill everyday
Lasts for five-ten years
Disadvantages:
Can make periods heavier and more painful
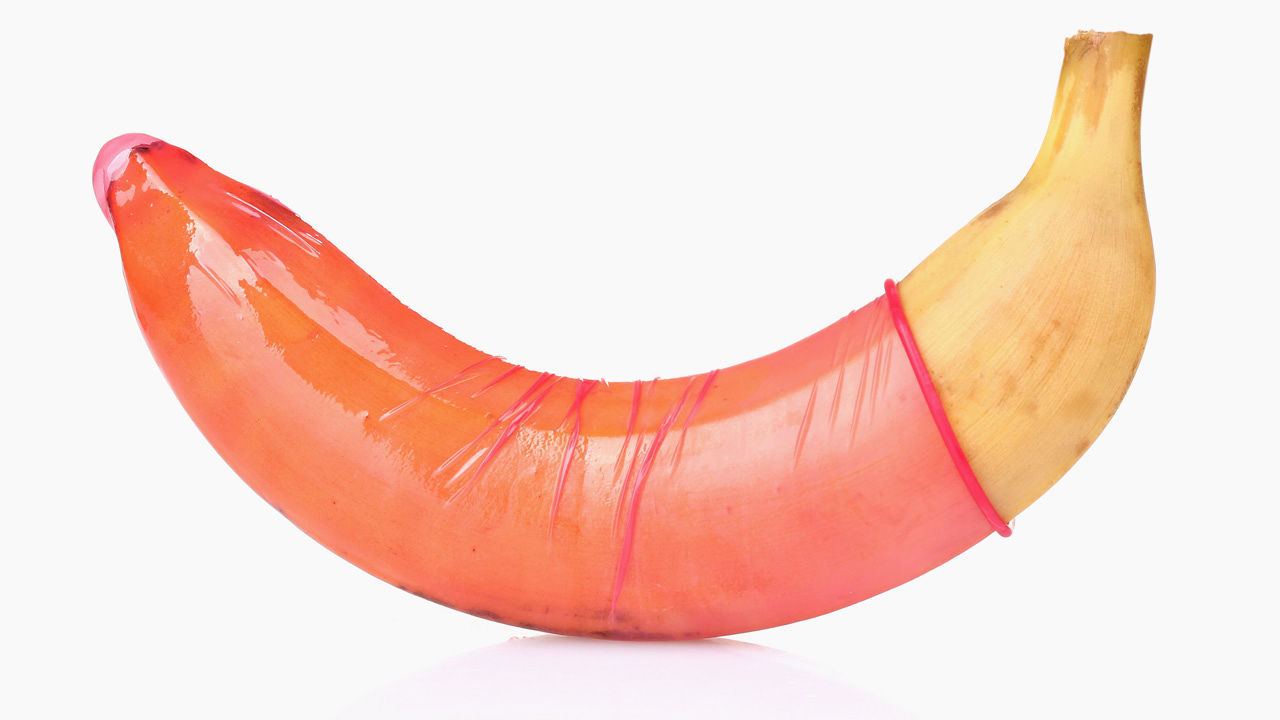

Male Condom
Condoms are placed over the penis before sex. They are 82% effective in preventing pregnancy with typical use.
Advantages:
Can prevent STIs
Disadvantages:
Need to put the condom on before sex but when the penis is erect
The penis needs to be withdrawn from the vagina before the erection is lost so that semen does not leak out
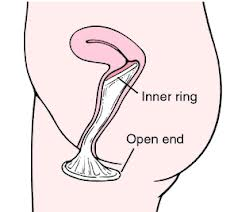 Female Condom
Female Condom
Female condoms are inserted into the vagina before sex. They are 79% effective in preventing pregnancy with typical use.
Advantages:
Can prevent STIs
Can be inserted anytime before sex
Disadvantages:
Can get pushed into the vagina during sex
The penis may slip between the condom and the vagina making this method ineffective
 Diaphragm/Cap with Spermicide
Diaphragm/Cap with Spermicide
The diaphragm is a flexible latex or silicone dome-shaped device filled with spermicide that is inserted into the upper vagina to cover the cervix and prevent pregnancy. The diaphragm is 88% effective at preventing pregnancy with typical use.
Advantages
Can be inserted at any time before sex (but don’t forget to use extra spermicide if it is left in for more than three hours)
Disadvantages
A correctly sized diaphragm needs to be used
It can take time to learn how to correctly insert the diaphragm
Must be left in for six hours after sex
Can increase the risk of urinary tract infections (UTIs)
For more information on Contraception choices go to our Contraception Page or visit your GP, local sexual health service, or GUM Clinic to discuss these options further.
Additionally, sexual health charities Brook and FPA have developed an interactive tool that can help you find out which methods of contraception may be best for you.The tool asks questions about your health, lifestyle, and contraceptive preferences. All your answers are completely confidential and cannot be linked back to you.
The tool is available on both charities’ websites:


